Verifying gasket compatibility for grooved pipe fittings in hot water HVAC loops prevents a range of avoidable problems in hydronic heating systems. Supply temperatures commonly hold between 140°F and 200°F, with certain commercial or older installations running sustained at 210–220°F near boilers. Standard EPDM gaskets serve reliably in many water services, yet prolonged exposure at elevated temperatures accelerates compression set, hardening, or swelling—particularly when glycol mixtures, corrosion inhibitors, or biocides enter the equation. Joints that pass initial pressure testing sometimes develop slow leaks months later, damaging insulation, staining ceilings, or triggering callbacks during peak heating season.
The verification routine starts early in the project cycle—during submittal review or material procurement—and continues through on-site inspection. Matching gasket ratings to actual system conditions, fluid makeup, and thermal cycling patterns delivers joints that maintain integrity over years of operation.
Why Compatibility Verification Matters in Hot Water Hydronic Loops
Hot water circuits place different demands on gaskets compared with chilled water lines. Temperatures stay higher for longer durations, return water rarely drops below 120°F in well-designed systems, and thermal expansion–contraction cycles impose repeated shear forces. Glycol antifreeze, used for freeze protection, introduces chemical interactions that standard compounds tolerate unevenly. Treatment chemicals further influence long-term performance.
A gasket lacking adequate heat resistance loses rebound capability after extended compression. Compression set creates micro-gaps that allow gradual fluid migration. Field observations from multiple hydronic projects show that joints operating continuously near 210°F with standard EPDM frequently exhibit signs of degradation within three to five heating seasons. Leaks tend to surface first on return legs or near vibration sources such as pumps. Thorough upfront checks eliminate these patterns and align with expectations for durable pressure boundaries in heating applications.
Gasket Materials and Temperature Capabilities in Grooved Couplings
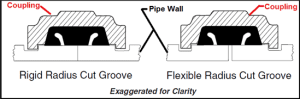
Grooved couplings depend on elastomeric gaskets to establish seals that tighten under system pressure. The gasket lips respond to internal force, flaring outward for enhanced contact.
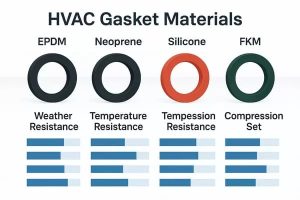
EPDM remains the primary choice for water-based services because of its resistance to water, flexibility across a wide range, and cost-effectiveness. Standard formulations generally cover -30°F to approximately 230°F intermittent, with continuous hot water service advised up to 180–200°F to maintain properties over time. Peroxide-cured or enhanced EPDM compounds push the continuous limit higher, frequently supporting 230–250°F in water without rapid loss of elasticity.
Silicone gaskets handle significantly higher temperatures—often 300–350°F in low-moisture or dry conditions—but see limited application in circulating hot water due to different compression behavior and higher cost. Nitrile compounds suit hydrocarbon fluids far better than hot water, where heat aging shortens service life considerably. Fluorocarbon options address aggressive chemicals but rarely appear in typical hydronic heating.
Temperature ratings derive from compound-specific data provided by manufacturers, distinguishing between maximum intermittent peaks and safe continuous exposure. In hot water HVAC service, operating close to or above the continuous threshold noticeably reduces expected gasket durability—sometimes cutting life expectancy in half for systems that run through extended winter periods.

Verification Steps in Practice
The process begins with accurate system documentation. Capture the maximum sustained temperature—not merely the design peak—along with minimum return temperature, working pressure range, fluid composition including glycol concentration and treatment additives, and anticipated thermal cycle frequency. These parameters set the reference point.
Cross-check against published gasket and coupling ratings from the manufacturer. Focus on statements specific to hot water service, glycol tolerance, and any adjustments for prolonged exposure. Temperature charts separate short-term peaks from long-term limits—prioritize the continuous rating for heating loops.
Examine the gasket for identification features. EPDM pieces often include color indicators—green for standard grades, red or alternate shades for high-temperature versions—along with compound codes, size designations, and occasional temperature notations. Visual confirmation verifies that the delivered gasket aligns with the specified material.
Verify dimensional compatibility in addition to material properties. Inner diameter, cross-section thickness, and lip configuration must correspond to the groove depth and pipe wall schedule. Discrepancies lead to uneven seating regardless of correct compound selection.
For applications with glycol above 30–50% or non-standard additives, obtain explicit chemical compatibility confirmation. Certain EPDM formulations resist swelling more effectively in glycol blends.
When system temperatures approach 220°F continuous, request aging test results or references from comparable installations to confirm performance margin.
Warning Signs and Observed Field Cases
Hardening after brief hot water exposure signals insufficient thermal stability. Excessive swelling or softening points to chemical incompatibility.
Real-world cases highlight the consequences. A mid-rise office building maintained 190–210°F supply temperatures; standard EPDM gaskets showed compression set after three winters, resulting in minor seepage at several couplings. Switching to a higher-rated peroxide-cured EPDM eliminated subsequent leaks across five additional seasons. In a healthcare facility operating at 220°F sustained, initial joints appeared sound, yet multiple couplings developed leaks after two heating periods due to gasket breakdown hastened by cycling and moderate glycol presence.
Similar outcomes recur in projects where temperatures border material limits without prior validation. Pump vibration transmits additional stress, and inadequate pipe restraint allows excess joint movement that accelerates fatigue in marginal gaskets.
Practical Approaches and Alternatives for Demanding Conditions
Pre-lubricated gaskets reduce assembly friction and promote uniform compression during torque application. Confirm that any lubricant remains compatible with hot water and system additives.
When standard EPDM ratings fall short, select high-temperature formulations clearly designated for elevated hot water service. Silicone provides reserve capacity in exceptional high-heat situations, though torque and joint geometry may require adjustment.
Incorporate routine inspections in high-stakes loops. Re-check bolt torque after initial relaxation and monitor for gasket discoloration, extrusion changes, or hardness variations during planned shutdowns.
Adequate pipe supports and expansion accommodations lessen mechanical loading on couplings, extending gasket service life irrespective of material grade.
About Hebei Jianzhi Foundry Group Co., Ltd.
Hebei Jianzhi Foundry Group Co., Ltd. commenced production in 1982 and has established itself as a principal manufacturer of grooved pipe fittings under the Jianzhi brand. Manufacturing bases in Tangshan, Hebei Province, and Chifeng, Inner Mongolia, support large-scale operations with considerable assets. The organization employs approximately 4500 personnel, including more than 350 engineers dedicated to technical development and quality control.
Certifications include ISO 9001 for quality management and ISO 14001 for environmental standards. The company holds over 200 patents and operates as a nationally recognized high-tech enterprise. Jianzhi contributes to standard setting, participating in six national standards, five industry standards, and four group standards, among them GB/T3287, GB/T9440, and GB/T25746.
The product range focuses on ductile iron grooved couplings, mechanical tees, crosses, flanges, and associated fittings produced to international specifications. These components deliver consistent performance in hydronic heating and HVAC applications. Distribution extends to more than 100 countries, underscoring sustained attention to casting accuracy and joint reliability.
Conclusion
Verification of gasket compatibility for grooved fittings in hot water HVAC loops removes many preventable issues from hydronic heating installations. Aligning material capabilities with real operating temperatures, fluid characteristics, and cycling demands produces joints that withstand years of service without degradation. Systematic checks during specification, procurement, and installation—paired with suitable material choices—cut down on leaks, lower maintenance requirements, and maintain efficient performance amid thermal and pressure variations.
FAQs
How do I check if an EPDM gasket suits hot water service in grooved HVAC fittings?
Examine the manufacturer’s sustained temperature rating for hot water—standard EPDM commonly limits to 180–200°F continuous, whereas enhanced grades extend to 230°F or beyond. Match against system maximums and inspect gasket color codes or compound markings for confirmation.
What temperature range can EPDM gaskets handle in hot hydronic heating loops?
Standard EPDM accommodates hot water up to roughly 180–230°F intermittent, with continuous duty best restricted below 200°F to preserve long-term properties. High-performance EPDM variants support reliable operation nearer 250°F in circulating water systems.
Is standard EPDM acceptable for 220°F hot water in grooved couplings?
Frequently not—prolonged exposure around 220°F exceeds typical standard EPDM thresholds, increasing the likelihood of compression set and eventual leakage after thermal cycles. High-temperature EPDM rated for that level becomes necessary.
How can I confirm grooved gasket compatibility with glycol in hot water loops?
Request manufacturer data specific to the glycol concentration and temperature. Certain EPDM formulations demonstrate superior resistance to swelling in glycol blends; chemical compatibility documentation proves essential when glycol surpasses 30–50%.
What signs indicate a gasket lacks proper rating for hot water temperature in grooved fittings?
Hardening, compression set, or cracking after exposure lead to gradual leaks, often appearing as pressure loss or weeping during heating season. Early indicators include gasket discoloration or reduced resilience at accessible joints.